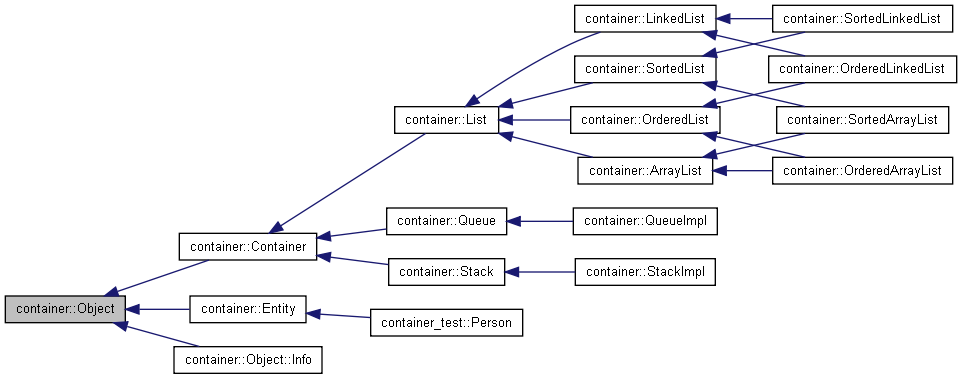
container::Object Class Reference
The root for most classes in the container namespace. More...
#include <object.h>
Classes | |
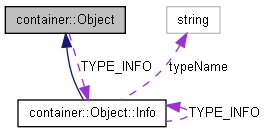
| class | Info |
| Metadata that describes type Object or a descendant there of. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual | ~Object () |
| virtual ostream & | renderState (ostream &os) const |
| Write the state of an Object for debugging and demonstration. | |
| virtual const Info * | typeInfo () const |
| Return the instance of Object::Info that describes the class of this object. | |
| virtual Object * | clone (bool deepCopy=false) const =0 |
| A polymorphic copy constructor. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static const Info *const | TYPE_INFO = Object::typeInfoFactory("Object") |
Protected Member Functions | |
| Object () | |
| Object (const Object &orig) | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static const Info * | typeInfoFactory (const string &typeName) |
| Create an instance of Object::Info. | |
Friends | |
| ostream & | operator<< (ostream &os, const Object &object) |
| Render the state of object as text. | |
| ostream & | operator<< (ostream &os, const Object *object) |
| Render the state of object as text. | |
Detailed Description
The root for most classes in the container namespace.Provides polymorphic behavior for rendering the state of an object. Default rendering is provided which prints "Object" followed by its memory address, i.e., the value of the 'this' pointer.
For customized output, objects may override Object::renderState(ostream&)const and Object::typeInfo(). One or both may be implemented. If, for example, a derived class does not have any state, it should at least override Object::typeInfo() so that it doesn't print as "Object".
Overriding these two methods takes the place of the standard pattern of creating a friend method for operator <<(ostream&, ...) in each class, with the advantage that references and pointers of a base-class type will produce output specific for the derived class. For example:
OrderedLinkedList* x = new OrderedLinkedList();
Entity * y = new Entity();
x->add(y);
Object* obj1 = x;
Object* obj2 = y;
cout << "[" << obj2 << "] is in [" << obj1 << "]";
Produces the following output
[Entity key(114) keyAsString(NULL)] is in [OrderedLinkedList count(1)
cursor->TAIL contents{[0]Entity key(114) keyAsString(NULL)}]
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| container::Object::Object | ( | const Object & | orig | ) | [protected] |
Member Function Documentation
| virtual Object* container::Object::clone | ( | bool | deepCopy = false |
) | const [pure virtual] |
A polymorphic copy constructor.
Implemented in container::ArrayList, container::Container, container::Entity, container::List, container::Object::Info, container::OrderedArrayList, container::OrderedLinkedList, container::OrderedList, container::Queue, container::QueueImpl, container::SortedArrayList, container::SortedLinkedList, container::SortedList, container::Stack, container::StackImpl, and container_test::Person.
| ostream & container::Object::renderState | ( | ostream & | os | ) | const [virtual] |
Write the state of an Object for debugging and demonstration.
This method must not change the state of an Object; adding or removing debug statements should not change the behavior of a class. The implementation must be robust, e.g., NULL safe, etc. and work without an unrecoverable error for any state, excluding an Object's time of construction and destruction. It is not required for the implementation to be thread safe.
- Precondition:
- The Object has been fully constructed and is not in the process of destruction
- Postcondition:
- The state of the Object is unchanged
Reimplemented in container::ArrayList, container::Container, container::Entity, container::LinkedList, container::List, container::Object::Info, container::OrderedArrayList, container::OrderedLinkedList, container::OrderedList, container::Queue, container::QueueImpl, container::SortedArrayList, container::SortedLinkedList, container::SortedList, container::Stack, and container::StackImpl.
00059 { 00060 // Casting 'this' to (const void*) prevents an infinite loop. 00061 return os << typeInfo()->typeName << " this(" << ((const void*)this) << ")"; 00062 }

| const Object::Info * container::Object::typeInfo | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Return the instance of Object::Info that describes the class of this object.
Instantiation of Object::Info is controlled by the protected method Object::typeInfoFactory(const string&). Each sub-class of Object should create one and only one instance of Object::Info.
Reimplemented in container::ArrayList, container::Container, container::Entity, container::LinkedList, container::List, container::Object::Info, container::OrderedArrayList, container::OrderedLinkedList, container::OrderedList, container::Queue, container::QueueImpl, container::SortedArrayList, container::SortedLinkedList, container::SortedList, container::Stack, container::StackImpl, and container_test::Person.
00064 { 00065 return TYPE_INFO; 00066 }

| const Object::Info * container::Object::typeInfoFactory | ( | const string & | typeName | ) | [static, protected] |
Create an instance of Object::Info.
Each sub-class of Object should create one and only one instance of Object::Info.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
| ostream& operator<< | ( | ostream & | os, | |
| const Object * | object | |||
| ) | [friend] |
Render the state of object as text.
Polymorphic behavior is achieved by calling Object::renderState(ostream&) on object. Parameter object is a pointer type and Object::renderState(ostream&) is a virtual method; therefore, a polymorphic determination is made as to which Object::renderState(ostream&) method to call. The determination is made at runtime (not compile time), and the winning candidate will be the method furthest down the inheritance chain with a matching signature.
This only works when an object is referred to by a pointer or by a reference.
00085 { 00086 if (object == NULL) 00087 // At this point there doesn't seem to be anyway to determine the 00088 // type of reference that was null. 00089 return os << "NULL"; 00090 else 00091 return object->renderState(os); 00092 }
| ostream& operator<< | ( | ostream & | os, | |
| const Object & | object | |||
| ) | [friend] |
Render the state of object as text.
Polymorphic behavior is achieved by calling Object::renderState(ostream&) on object. Parameter object is a reference type and Object::renderState(ostream&) is a virtual method; therefore, a polymorphic determination is made as to which Object::renderState(ostream&) method to call. The determination is made at runtime (not compile time), and the winning candidate will be the method furthest down the inheritance chain with a matching signature.
This only works when an object is referred to by a pointer or by a reference.
00076 { 00077 if (&object == NULL) 00078 // At this point there doesn't seem to be anyway to determine the 00079 // type of reference that was null. 00080 return os << "NULL"; 00081 else 00082 return object.renderState(os); 00083 }
Member Data Documentation
const Object::Info *const container::Object::TYPE_INFO = Object::typeInfoFactory("Object") [static] |
Reimplemented in container::ArrayList, container::Container, container::Entity, container::LinkedList, container::List, container::Object::Info, container::OrderedArrayList, container::OrderedLinkedList, container::OrderedList, container::Queue, container::QueueImpl, container::SortedArrayList, container::SortedLinkedList, container::SortedList, container::Stack, container::StackImpl, and container_test::Person.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
 1.5.9
1.5.9